Haendel: Le Messie
Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa | Su |
Concert in English with French surtitles
Synopsis
In Christian theology, the Messiah is the saviour of humankind. The Messiah (Māšîaḥ) is an Old Testament Hebrew word meaning "the Anointed One", which in New Testament Greek is Christ, a title given to Jesus of Nazareth, known by his followers as "Jesus Christ". Handel's Messiah has been described by the early-music scholar Richard Luckett as "a commentary on [Jesus Christ's] Nativity, Passion, Resurrection and Ascension", beginning with God's promises as spoken by the prophets and ending with Christ's glorification in heaven. In contrast with most of Handel's oratorios, the singers in Messiah do not assume dramatic roles; there is no single, dominant narrative voice; and very little use is made of quoted speech. In his libretto, Jennens's intention was not to dramatise the life and teachings of Jesus, but to acclaim the "Mysteryof Godliness", using a compilation of extracts from the Authorized (King James) Version of the Bible, and from the Psalms included in the 1662 Book of Common Prayer.
The three-part structure of the work approximates to that of Handel's three-act operas, with the "parts" subdivided by Jennens into "scenes". Each scene is a collection of individual numbers or "movements" which take the form of recitatives, arias and choruses. There are two instrumental numbers, the opening Sinfony in the style of a French overture, and the pastoral Pifa, often called the "pastoral symphony", at the mid-point of Part I.
In Part I, the Messiah's coming and the virgin birth are predicted by the Old Testament prophets. The annunciation to the shepherds of the birth of the Christ is represented in the words of Luke's gospel. Part II covers Christ's passion and his death, his resurrection and ascension, the first spreading of the gospel through the world, and a definitive statement of God's glory summarised in the Hallelujah. Part III begins with the promise of redemption, followed by a prediction of the day of judgment and the "general resurrection", ending with the final victory over sin and death and the acclamation of Christ. According to the musicologist Donald Burrows, much of the text is so allusive as to be largely incomprehensible to those ignorant of the biblical accounts. For the benefit of his audiences Jennens printed and issued a pamphlet explaining the reasons for his choices of scriptural selections.
Program and cast
VIP CATEGORY: Best seats in house with complimentary glass of champagne and programme.
PRESTIGE CATEGORY: Excellent seats with complimentary glass of champagne and programme.
Marie Lys: Soprano
Nicolò Balducci: Countertenor
Rémy Burnens: Tenor
Halidou Nombre* Barytone
*Member of the Académie de l'Opéra Royal
Chœur de l’Opéra Royal
Orchestre de l’Opéra Royal
Under the patronage of Aline Foriel-Destezet
Gaétan Jarry: Conductor
Royal Chapel of Versailles
The Royal Chapel was finished in 1710 at the end of Louis XIV’s reign. Jules Hardouin-Mansart proposed the plan to the King in 1669. The First Architect died in 1708 without seeing the end of the works which were taken over by his brother-in-law Robert De Cotte. The reigning monarch only came for major religious festivals where he received communion, for ceremonies of the Order of Saint-Esprit, for the baptisms and weddings of the royal children celebrated from 1710 to 1789. This exceptional palatine chapel was also used for a wide range of religious ceremonies, including the marriage of Archduchess Marie-Antoinette with the future Louis XVI.
Above the altar, around the organ by Clicquot decorated with a fine relief of King David, played by great masters like François Couperin, the Chapel’s music, famous all over Europe, sung motets everyday during all religious services. Today Handel’s Dixit Dominus or Messiah, Bach’s Oratorios, Magnificat, Cantatas or Passions, Pergolesi’s Stabat Mater or Charpentier’s Te Deum ring out in this majestic architecture.

 EN
EN DE
DE IT
IT FR
FR ES
ES RU
RU JP
JP RO
RO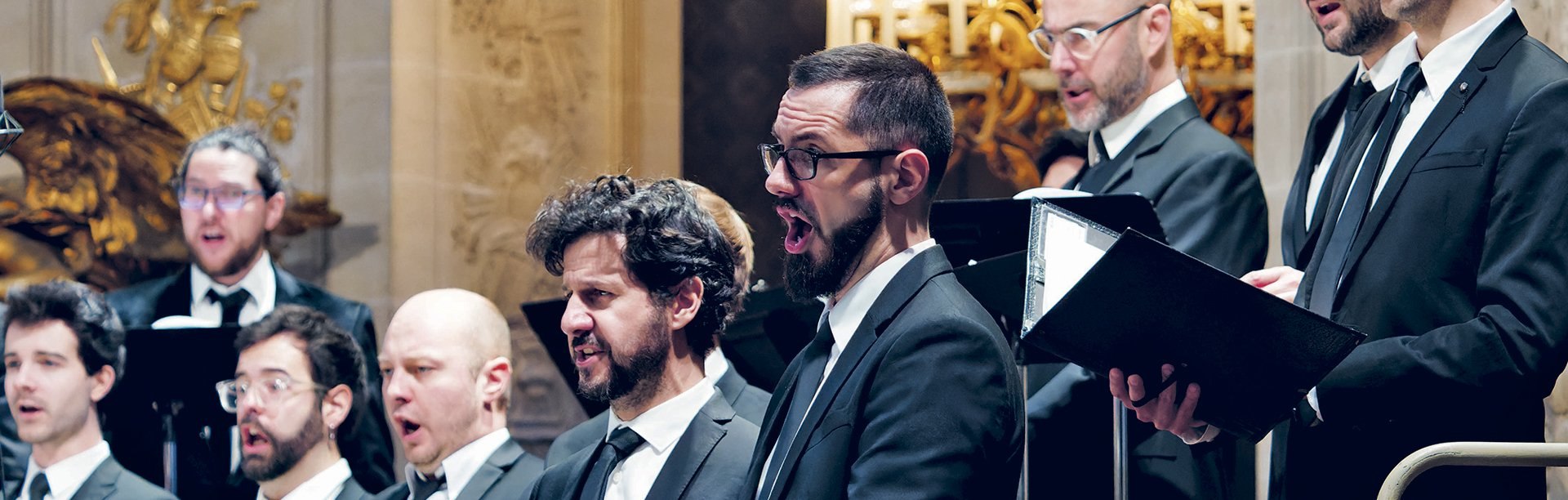
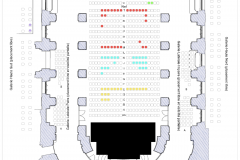 Seating plan
Seating plan 